When you visit a merchant by clicking a link on this site we may make a commission on anything you buy (at no additional cost to you). Affiliate programs and affiliations include, but are not limited to Amazon Associates and the eBay Partner Network.”
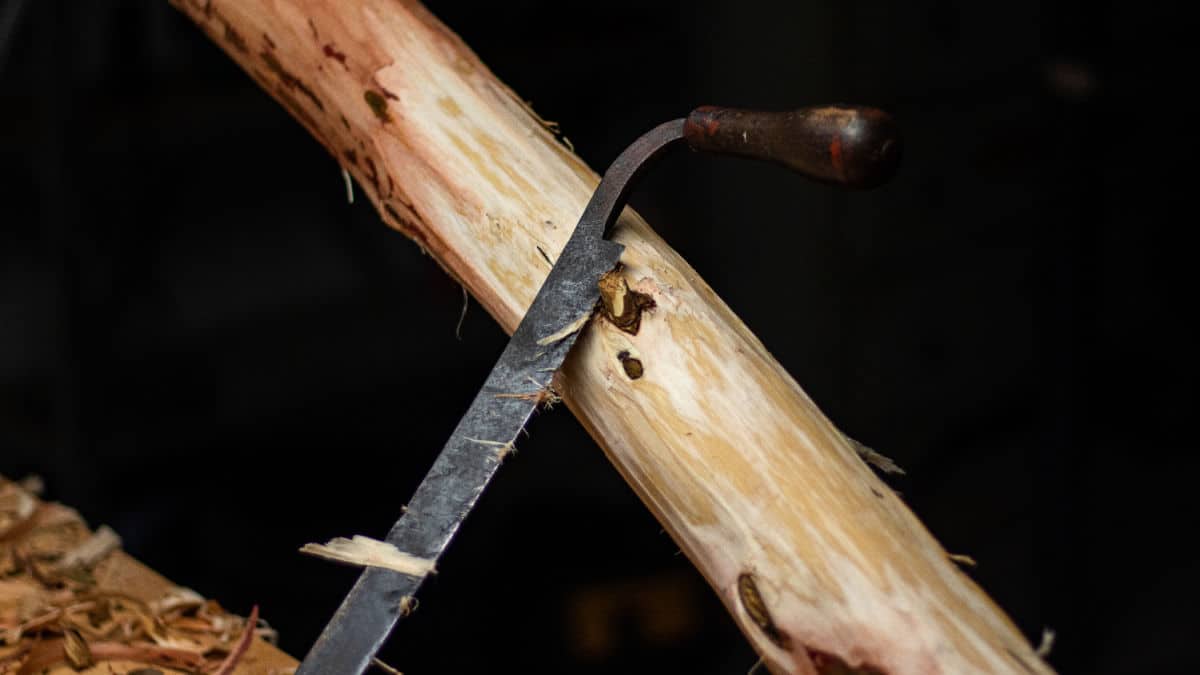
A draw knife is a versatile and traditional woodworking tool that has been used for centuries to shape wood by removing layers or making precise cuts. Consisting of a long, thin blade with two handles on either end, the draw knife enables woodworkers to delicately carve and shape wood for various applications, including removing bark from branches, shaping handles, spokes, spindles, and crafting curved furniture components such as cabriole legs.
The blade of a draw knife comes in a variety of lengths and shapes, depending on its intended purpose, with most ranging from 8-10 inches in length. Craftsmen often choose their draw knife based on the specific woodworking tasks they need to accomplish. For instance, larger draw knives are suitable for more robust tasks such as peeling bark or hewing small logs. In contrast, smaller models are fit for specialty purposes like coopering or creating chair seats.
Using a draw knife involves applying even pressure and control to glide the tool across the surface of the wood, resulting in thin shavings being removed. Depending on the angle and the amount of pressure applied, a woodworker can make deep cuts or produce fine shavings to achieve the desired level of detail in their work. Today, draw knives continue to be indispensable tools for woodworkers who appreciate their versatility, precision, and the tactile experience they offer when crafting distinctive wooden pieces.
What Is a Draw Knife
A draw knife is a traditional woodworking hand tool used to shape wood by removing shavings. It consists of a blade with a handle at each end, which allows for precise control and manipulation of the tool while shaping wood. The blade is typically much longer along the cutting edge than it is deep, from the cutting edge to the back edge. The draw knife is pulled, or “drawn,” towards the user, hence the name.
Draw Knife Components
Blade: The blade of a draw knife is the primary component responsible for cutting and shaving the wood. It can come in various lengths and shapes, depending on its intended purpose. The cutting edge of the blade is sharp and straight, allowing for efficient removal of material from the workpiece.
Handles: The handles of a draw knife are located at each end of the blade. These ergonomic handles provide the user with the ability to securely grip and control the tool while it is in use. The position of the handles allows the user to apply even pressure and create smooth, uniform shavings from the wood.
The draw knife is a versatile and essential tool in woodworking, with a variety of applications such as debarking trees, creating thin shavings, and shaping handles or spokes. With its sharp, straight blade and effective control provided by the handles, it enables woodworkers to shape materials with precision and ease.
Types of Draw Knives
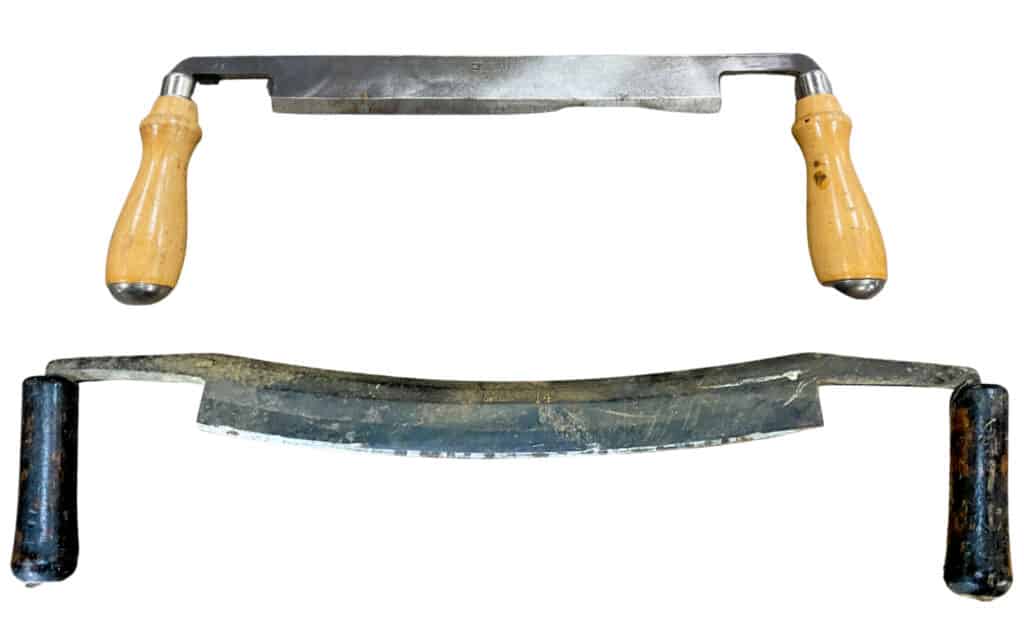

There are two popular types of draw knives that cater to different woodworking needs, and each type serves a unique purpose in helping woodworkers shape, shave, or remove wood.
Straight Draw Knives
The Straight Draw Knives are designed for general woodworking tasks, such as planing logs, chamfering, and shaving wood. These knives have a straight blade that can range from 20 to 35 cm in length, ensuring even cuts and clean shavings (source). Woodworkers prefer using straight draw knives for precision and control as they provide better visibility when working on a task.
When it comes to sharpening, straight draw knives should be sharpened frequently to maintain their cutting edge. Use a sharpening stone or a strop for optimal results.
Key features of straight draw knives include:
- Blade length: 20-35 cm
- Used for general woodworking tasks
- Better precision and control
Curved Draw Knives
Curved Draw Knives are specialized for more challenging woodworking tasks, such as removing bark, creating deeper cuts, and sculpting wood source. The curved blade of these knives allows woodworkers to work with more significant wood removals, as it conforms more naturally to the contours of the material being worked on.
Sharpening curved draw knives can be a bit more complicated compared to straight knives, but it is essential to maintain their cutting potential. Curved knives should also be sharpened using a sharpening stone or a strop, following the curve of the blade throughout the process.
Key features of curved draw knives include:
- Blade with a horizontal curve
- Designed for challenging woodworking tasks
- Efficient for more significant wood removals
Both straight and curved draw knives are invaluable tools for woodworkers when it comes to working with various projects. Whether you need precise cuts using a straight draw knife or aggressive material removal with a curved one, these tools provide the versatility required in the world of woodworking.
Uses and Applications
Shaping and Detailing
A draw knife is a highly versatile tool used by woodworkers for a variety of purposes. One of its main uses is for shaping and detailing wood by removing shavings to create smooth surfaces, curves, and other intricate designs. This makes it an invaluable tool for tasks such as creating customized handles, spokes, or other detailed woodworking projects. The draw knife generally consists of a long thin blade fixed between two handles, with the length of the blade often ranging from 8 to 10 inches.
Safety is crucial when working with a draw knife, as the sharp blade can cause injury if not handled properly. Woodworkers should always use proper techniques and protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection, to minimize risks.
Debarking Trees
Another common application for draw knives is debarking trees. The long, thin blade allows for efficient removal of bark without causing unnecessary damage to the tree. This is especially useful for preparing logs for construction, woodworking, or other purposes where a clean, smooth surface is desired.
Debarking trees with a draw knife is a relatively simple process, but it does require some skill and patience. Woodworkers must ensure that the blade remains sharp, as a dull or rust-covered blade can result in uneven cuts or damage to the wood.
The versatility of a draw knife is one of the reasons it continues to be a popular tool among woodworkers. Its ability to handle intricate detailing as well as a more demanding task like debarking trees showcases its flexibility and usefulness in various woodworking projects.
Selecting the Right Draw Knife
Blade Thickness and Design
When choosing a drawknife, considering the blade thickness and design is crucial to finding the right tool for your woodworking needs. Draw knives come in various thicknesses, and the optimal choice depends on the type of work you need it for. Thicker blades are more durable and offer better support for heavy-duty cutting tasks, while thinner blades allow for greater accuracy and precision.
In addition to thickness, take note of the drawknife’s overall design when making a decision. Both straight and curved blades are available, with straight blades generally used for flatter surfaces and curved blades for deeper cuts and bark removal. A high-quality blade is essential for maintaining sharpness and durability over time, ensuring your drawknife remains a valuable asset in your woodworking toolkit.
Handle Design
The handle design of a drawknife is another factor that can impact its usability and function. Look for ergonomic handles that allow for comfortable and secure grip during extended use periods, leading to a more enjoyable woodworking experience. Handles are typically made of wood or composite materials and come in different shapes and sizes. Your preference may vary, but it’s essential to find a handle design that fits your hand and enables you to maintain control and accuracy.
To recap, when selecting the right draw knife, consider the blade thickness, blade design, and handle design. Opt for a high-quality and durable blade that suits your woodworking needs, and don’t forget to ensure that the handle provides an ergonomic grip for optimum control and accuracy during use. By taking these factors into account, you will be better equipped to choose the perfect drawknife for your woodworking projects.
Maintenance and Safety
When it comes to maintaining and using draw knives safely, there are a few aspects to consider. This section will outline two sub-sections: Sharpening and Cleaning, Safe and Proper Use.
Sharpening and Cleaning
Sharpening your draw knife is crucial for efficient and safe use. A dull blade can be more dangerous than a sharp one, as it requires more force to use, increasing the risk of accidents. To sharpen a draw knife, use a sharpening stone or a fine-grit sandpaper. Start by wetting the stone, if necessary, or use a dry sharpening method if recommended for the specific type of stone. Hold the draw knife at the appropriate angle and move it along the stone or sandpaper in a smooth motion. Take care of the beveled side first, then the flat side to create or maintain a secondary bevel. Repeat the process until the blade reaches the desired sharpness.
Cleaning is also essential to prolong the lifespan and effectiveness of a draw knife. Dirt or deposits on a blade can affect its cutting ability and increase the risk of rust. To clean a draw knife, wipe it down with a cloth after each use. Occasionally, you may need to use a mild detergent or a specialized cleaning solution to remove stubborn dirt or grime. After cleaning, apply a light coat of oil to prevent rust and keep the blade well-protected.
Safe and Proper Use
When using a draw knife, following proper technique and safety guidelines is vital. Here are some tips for safe and secure operation:
- Power tools: While draw knives are manual cutting tools, power tools like a saw can help with initial shaping or cutting tasks before using the draw knife. This can save time and effort and reduce the risk of injury.
- Curves: A draw knife is suitable for creating various shapes, including curves. Choose a draw knife with a curved blade when working on curved surfaces or designs, as it will work better than a straight blade in these situations.
- Peel: One of the primary uses of a draw knife is to peel bark off logs, so make sure to select a draw knife with a proper hardness and length suitable for this task.
- Cutting tool: Always keep in mind that a draw knife is a cutting tool, not a chisel or a saw. It is designed for shaving or shaping wood and does not work well for making deep cuts, crosscuts, or splitting wood.
- Body positioning: Ensure that your body is positioned correctly and safely when using a draw knife. Keep elbows tucked in, and maintain a firm grip on the handles. Your body positioning will act as a safety stop, preventing the blade from slipping and causing injuries.
Following these maintenance and safety guidelines will help you use and preserve your draw knife effectively and safely, ensuring a smooth woodworking experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the draw knife remains an indispensable tool in woodworking due to its versatility and precision. Its various applications require careful selection based on blade design and handle comfort. The two main types, straight and curved draw knives, cater to different needs, from debarking trees to shaping intricate designs. Maintenance and safe use, including regular sharpening and correct body positioning, are essential for an optimal woodworking experience. A high-quality draw knife, selected and used appropriately, can be a rewarding asset in any woodworker’s toolkit.
Do Sheepsfoot Blades Have A Purpose? (Cuz They’re Ugly…)
Spetsnaz Machetes – Blades Of The Russian Special Forces
What Is The Actual Purpose Of A Spear Point Knife Blade?
CRKT CEO Review – Coolest, Most Worthless Knife Ever?
How Sharp Is A Scalpel? (Is It Sharper Than A Razor?)
Can You Shave With A Knife? (Yes, Here’s How)
When you visit a merchant by clicking a link on this site we may make a commission on anything you buy (at no additional cost to you). Affiliate programs and affiliations include, but are not limited to Amazon Associates and the eBay Partner Network.”